Sometimes, you may find yourself in a situation where you need to delete all files in a directory or simply clean up a directory by removing all files except those with a specific extension (e.g., files ending with a particular type).
In this article, we will show you how to delete files in a directory, excluding certain file extensions or types, using the rm, find, and globignore commands.
Before we move any further, let us start by briefly having a look at one important concept in Linux – filename pattern matching, which will enable us to deal with our issue at hand.
In Linux, a shell pattern is a string that consists of the following special characters, known as wildcards or metacharacters:
*– matches zero or more characters?– matches any single character[seq]– matches any character inseq[!seq]– matches any character not inseq
There are three possible methods we shall explore here, and these include:
Delete Files Using Extended Pattern Matching Operators
The extended pattern matching operators are listed below. In this case, pattern-list refers to one or more filenames, separated using the | character:
*(pattern-list)– matches zero or more occurrences of the specified patterns?(pattern-list)– matches zero or one occurrence of the specified patterns- +(pattern-list) – matches one or more occurrences of the specified patterns
@(pattern-list)– matches one of the specified patterns!(pattern-list)– matches anything except one of the given patterns
To use them, enable the extglob shell option as follows:
shopt -s extglob
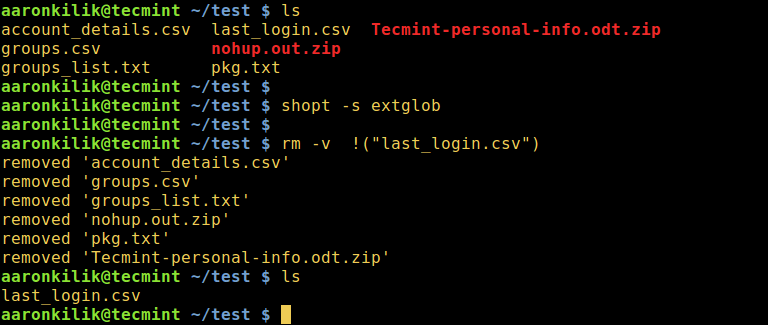
1. To delete all files in a directory except a specific file, type the following command:
rm -v !("filename")
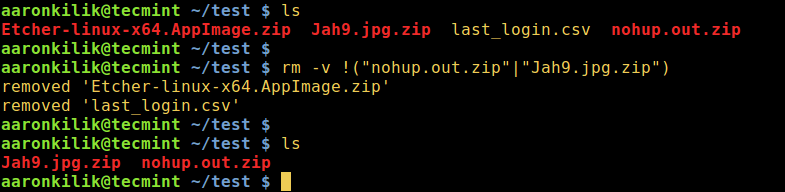
2. To delete all files with the exception of filename1 and filename2:
rm -v !("filename1"|"filename2")
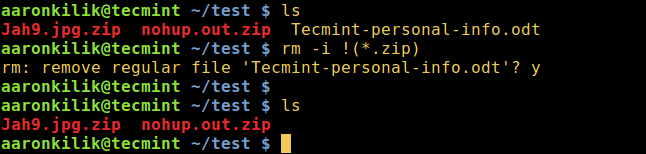
3. To remove all files except for .zip files, interactively:
rm -i !(*.zip)
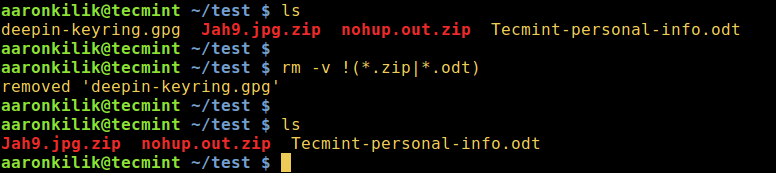
4. To delete all files except for .zip and .odt files while displaying the actions being performed:
rm -v !(*.zip|*.odt)
Once you have all the required commands, turn off the extglob shell option like so:
shopt -u extglob
Delete Files Using Linux find Command
Under this method, we can use find command exclusively with appropriate options or in conjunction with the xargs command by employing a pipeline as in the forms below:
find /directory/ -type f -not -name 'PATTERN' -delete
find /directory/ -type f -not -name 'PATTERN' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm {}
find /directory/ -type f -not -name 'PATTERN' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm [options] {}
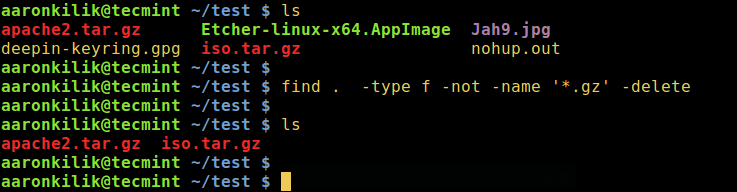
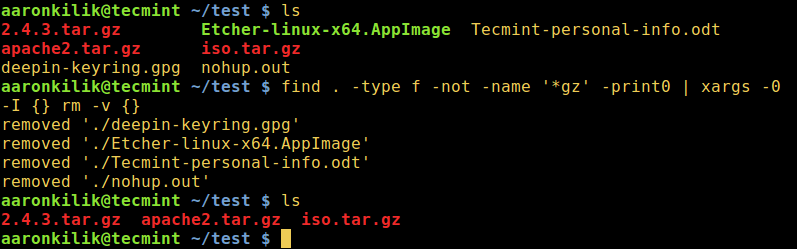
5. The following command will delete all files apart from .gz files in the current directory:
find . -type f -not -name '*.gz'-delete
6. Using a pipeline and xargs, you can modify the case above as follows:
find . -type f -not -name '*gz' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm -v {}
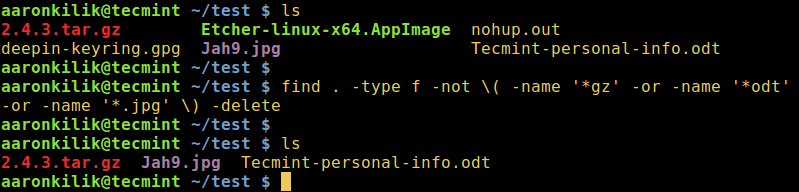
7. Let us look at one additional example, the command below will wipe out all files excluding .gz, .odt, and .jpg files in the current directory:
find . -type f -not (-name '*gz' -or -name '*odt' -or -name '*.jpg' ) -delete
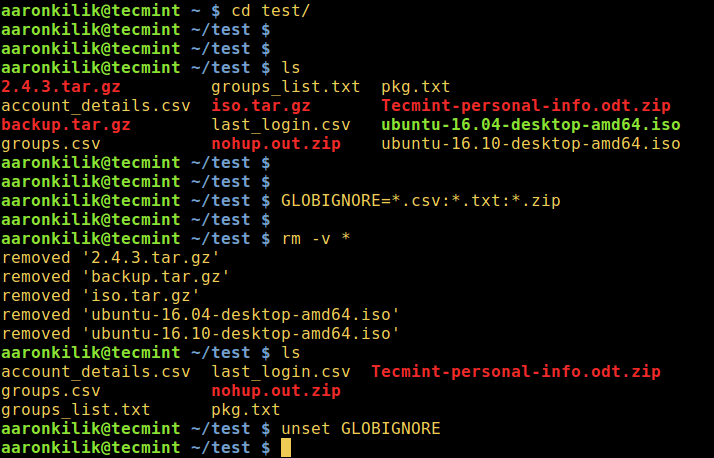
Delete Files Using Bash GLOBIGNORE Variable
This last approach, however, only works with bash. Here, the GLOBIGNORE variable stores a colon-separated pattern-list (filenames) to be ignored by pathname expansion.
To employ this method, move into the directory that you wish to clean up, then set the GLOBIGNORE variable as follows:
cd test GLOBIGNORE=*.odt:*.iso:*.txt
In this instance, all files other than .odt, .iso, and .txt files with be removed from the current directory.
Now run the command to clean up the directory:
rm -v *
Afterwards, turn off GLOBIGNORE variable:
$ unset GLOBIGNORE
Note: To understand the meaning of the flags employed in the commands above, refer to the man pages of each command we have used in the various illustrations.
Conclusion
These are a few simple and effective ways to delete files in Linux, keeping only those with specific extensions or filenames intact. If you know of any other useful command-line techniques for cleaning up directories, feel free to share them in the feedback section below.