Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, you will:
- Schedule PowerCLI and Python scripts for recurring automation.
- Use Windows Task Scheduler to run scripts without manual intervention.
- Apply best practices for reliability, security, and maintainability in VMware automation.
My Personal Repository on GitHub
VMware Repository on GitHub
Prerequisites
- Completed Articles 1–6.
- PowerCLI, Python, and previous scripts tested and available on your automation host.
- Access to Windows Task Scheduler or an equivalent scheduling tool.
1. Why Schedule VMware Scripts?
Routine tasks like VM snapshots, reporting, backups, and audits are time-consuming if performed manually.
Scheduling scripts lets you automate these tasks consistently, freeing up time and reducing human error.
2. Using Windows Task Scheduler for Automation
Windows Task Scheduler is a built-in tool to run scripts on a schedule (daily, weekly, etc).
Example: Schedule a PowerCLI Script
Step 1: Prepare Your Script
Next up: In Article 8, you will dive into advanced VM, NSX, and Aria Operations automation with practical PowerCLI and Python scripting examples.
Step 2: Open Task Scheduler
- Press
Win + R, typetaskschd.msc, and hit Enter.
Step 3: Create a New Task
- Select “Create Task”.
- Give it a descriptive name (e.g., “Daily VMware Report”).
- Under “Security Options”, select “Run whether user is logged on or not”.
Step 4: Set the Trigger
- Go to the “Triggers” tab and set the schedule (e.g., daily at 6:00 AM).
Step 5: Set the Action
- Go to the “Actions” tab.
- Click “New”.
- Set “Program/script” to:
powershell.exe - Set “Add arguments” to:
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:Automationvm_report.ps1"
Step 6: Save the Task
- Click OK, enter your credentials, and ensure the task is enabled.
Example: Schedule a Python Script
- Follow the same steps, but set “Program/script” to the path of your
python.exe, and “Add arguments” to your script path:"C:PathTopython.exe""C:Automationmy_python_script.py"
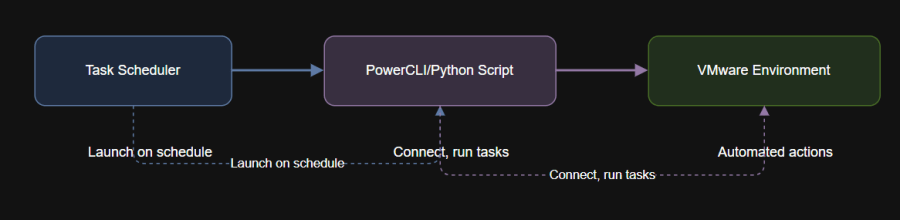
3. Diagram: Scheduling and Automation Workflow
4. Best Practices for Safe and Reliable VMware Automation
- Credential Management:
Use Windows Credential Manager or encrypted credential files instead of hardcoding passwords. - Script Logging:
Ensure all scripts write logs for auditing and troubleshooting. - Testing:
Always test in a lab or on non-critical systems before deploying to production. - Alerting:
Set up email notifications for script failures using Task Scheduler’s “On failure” actions or via your scripts. - Idempotency:
Scripts should be safe to re-run without unintended side effects (e.g., check for existing snapshots before creating new ones). - Documentation:
Maintain comments and change logs in your scripts for future reference.
5. Troubleshooting Tips
- If scripts do not run as scheduled, check Task Scheduler history for error codes.
- Make sure the task user account has permission to run PowerShell/Python and access network resources.
- Use full paths for all files in your scripts to avoid “file not found” errors.
- For scripts that hang, set a timeout in your Python
subprocess.run()calls.
6. Further Reading
7. Conclusion and Next Steps
Make sure your PowerShell script (e.g., vm_report.ps1) is working and located at a path like C:Automationvm_report.ps1.
You have learned how to schedule VMware automation scripts and apply best practices for reliability, security, and maintainability.
This enables consistent, automated operations and helps you scale your infrastructure management.