Learning Objectives
Now, use Python to call that script. Here’s a basic example:
- Understand the differences and similarities between PowerShell, PowerCLI, and Python.
- Learn basic scripting structures in PowerShell and Python.
- Execute your first script that combines Python and PowerCLI to automate a simple VMware task.
My Personal Repository on GitHub
# List VMs and output to file
Get-VM | Select-Object Name, PowerState | Out-File -FilePath C:Tempvm_list.txt
Prerequisites
- Completed Article 1 (PowerCLI and Python are installed).
- Access to a VMware vSphere environment (lab or production).
- A Windows system (PowerCLI requires Windows PowerShell).
1. PowerShell, PowerCLI, and Python — How They Work Together
- PowerShell: A Windows command-line shell and scripting language.
- PowerCLI: A set of modules that plug into PowerShell, letting you control VMware vSphere, NSX, and Aria with simple commands.
- Python: A versatile scripting language, popular for orchestrating and extending automation.
Example:
2. Basic Syntax: PowerShell vs Python
PowerShell Basics
- Cmdlets start with a verb-noun pattern (
Get-VM,Start-VM). - Variables use
$. - Comments start with
#.
Replace <vcenter-address>, <username>, and <password> with your real values.
Replace <vcenter-address>, <username>, and <password> with your real values.
By the end of this article, you will:
3. Your First Automated Task: Calling PowerCLI from Python
You’ve learned the basics of both PowerShell and Python, and you’ve seen how to use Python to execute a PowerCLI script. This opens up a world of automation possibilities, you can now combine VMware commands with Python’s data handling and logic.
Step 1: Create a PowerShell Script
You can run PowerCLI cmdlets directly in PowerShell, or orchestrate more complex logic by having Python scripts call PowerShell commands. # Print the output (if any) Example:# List of VM names
vm_list = ['Web01', 'App01', 'DB01']# List all VMs
Get-VMThe simplest way for Python to interact with PowerCLI is by executing PowerShell scripts from within a Python program.Legend:
Step 2: Execute PowerShell Script from Python
print("Script Output:", completed_process.stdout)
if completed_process.stderr:
print("Errors:", completed_process.stderr)import subprocessLet’s start by writing a script that lists all VMs and saves them to a text file.Save this as
list_vms.ps1:
4. Diagram: Workflow — Python Driving PowerCLI
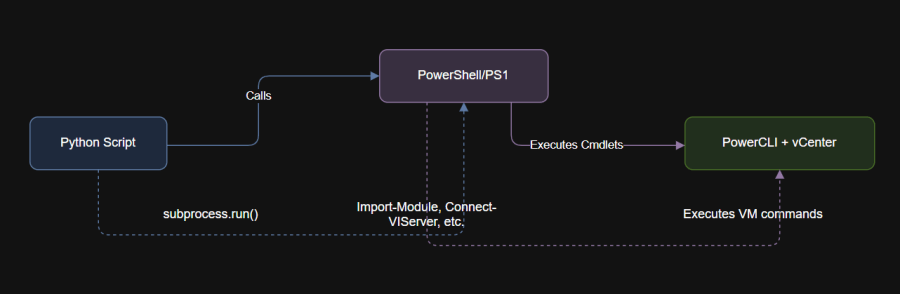
# Import PowerCLI
Import-Module VMware.PowerCLIIn Article 3, you’ll connect to vCenter and retrieve detailed VM info using this combined approach.